Landslide Tools
Explore additional tools and resources related to landslides.
Landslides are a significant hazard in West Virginia, particularly in the Central Allegheny Plateau and Cumberland Plateau/Mountains regions, due to steep slopes, loose soils, and less resistant bedrock. While heavy rainfall and snowmelt often trigger landslides, human activities like mining or other land disturbances also contribute to slope instability.
West Virginia's landslide risk tools and resources primarily focus on identifying high-risk areas for community hazard mitigation planning, rather than predicting specific landslide events. A brochure is also provided to help homeowners recognize potential landslide risks on their property.
Outreach Materials to Mitigate Landslide Risks
-
Brochures
- Community: Mitigating Landslide Risk through Planning
- Homeowner: Recognizing Landslide Risk on Your Property
- Story Maps
Web Tools showing Landslide Incidents and Susceptibility:
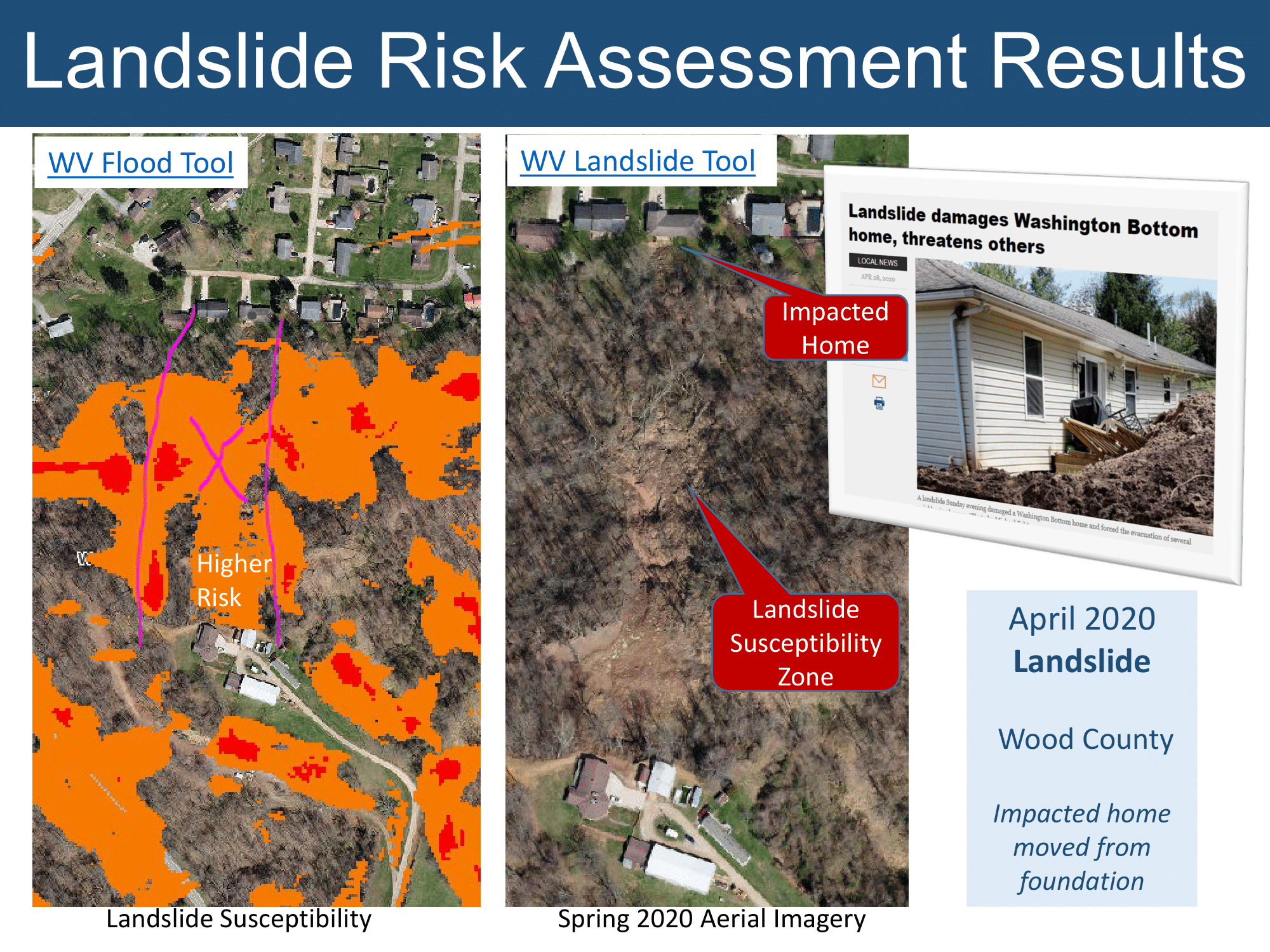
- WV Landslide Tool
- WV Flood Tool's Risk MAP View (Turn on landslide layers)
Statewide Landslide Incident Inventory:
- Inventoried 196,302 landslide features from LiDAR mapping (106,399) and other sources (89,903)
- Mapped landslide types: slides, debris flows, lateral spreads, rocks falls, and multiple failures
- Most common landslides mapped are slides and slumps (98%)
- The nature of the West Virginia landscape and the LiDAR imagery limited mapping to landslides at least 33 feet wide
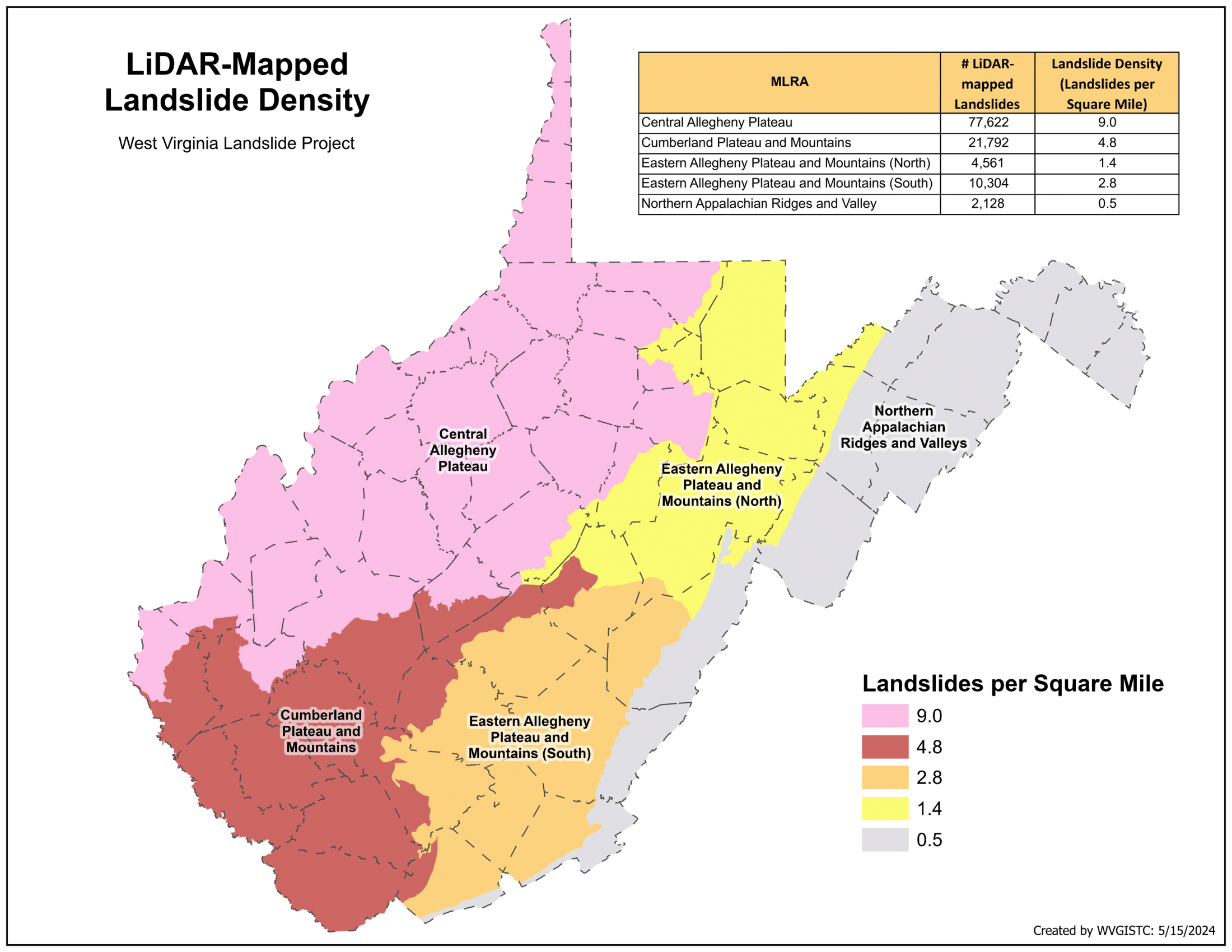
Landslide Inventory Assessment by Major Land Resource Areas (MLRAs):
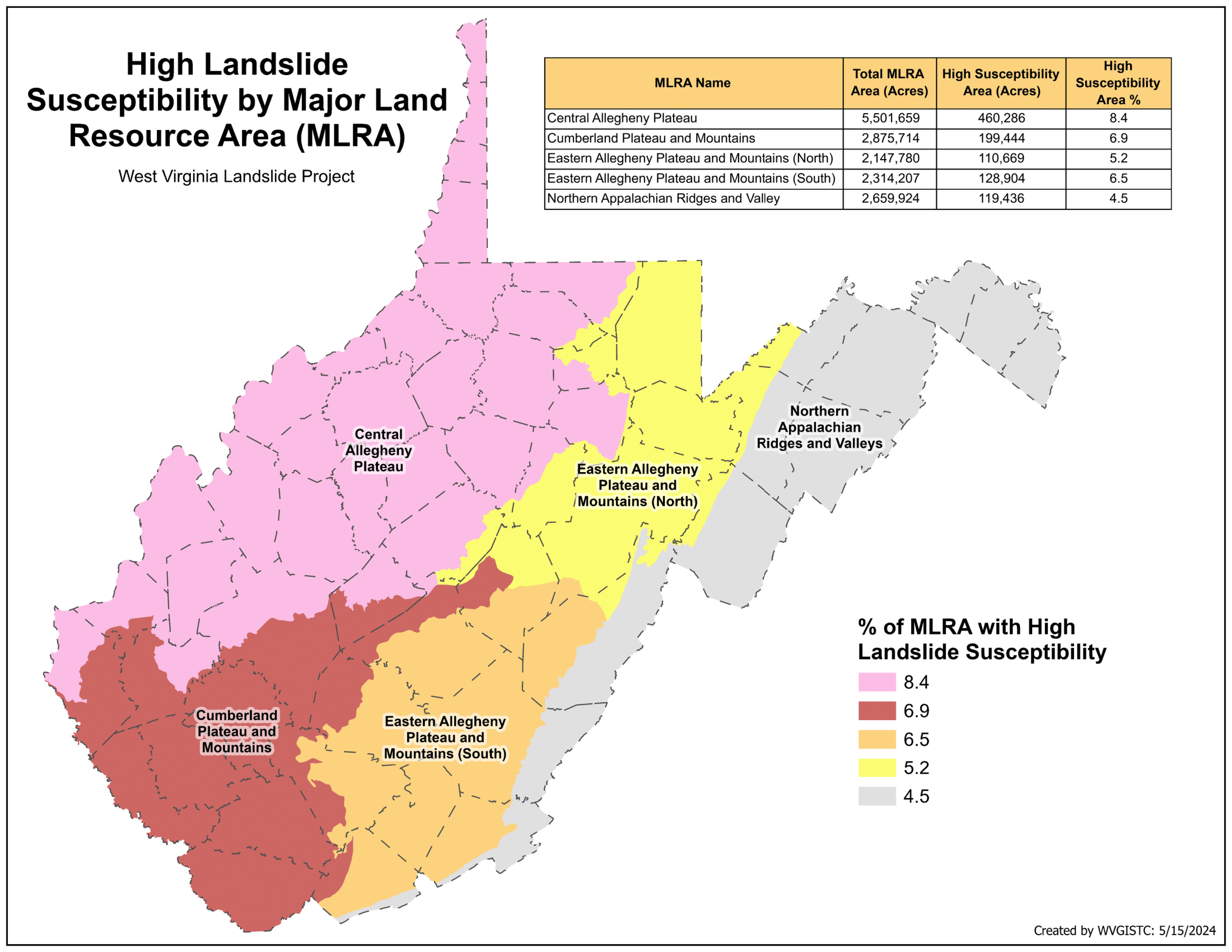
Statewide Landslide Susceptibility:
- A statewide Landslide susceptibility grid of 2-meter resolution was generated using machine learning-based slope prediction methodology
- Statewide landslide risk assessment was created for geographically associated major land resource areas (MLRAs) to minimize heterogeneity in physiographic conditions that may influence landslide susceptibility
Susceptibility is classified according to low, medium, and high probability of slope failure:
- Low Risk: 0-30% probability of slope failure
- Medium Risk: 30-70% probability of slope failure
- High Risk: 70-100% probability of slope failure
- WV Landslide Susceptibility Maps: High Susceptibility | Medium-to-High Susceptibility
- Landslide Factors and Predictors: Slope, soil type, and bedrock geology. Steeper slopes, unconsolidated soils, and less resistant rock units like shale and siltstone increase landslide susceptibility.
- A published paper reveals that topographic variables such as slope angle, slope curvature, and topographic roughness are important indicators of landslide susceptibility.
Landslide Assessment Products and Data:
Presentations:
Limitations and Disclaimer:
This landslide risk assessment study is limited to a county-level analysis, suitable only for planning purposes and not site-specific analysis or remediation. For detailed or specific landslide analyses, professionals like engineers and geologists should be consulted.